- 前言:
本次爬取的是新浪微博移动端(https://m.weibo.cn/),爬取的数据是用户微博首页的第一条微博(如下图),包括文字内容、转发量、评论数、点赞数和发布时间,还有用户名和其所在地区(后面可以分析不同地区微博用户的关心的热点话题)。

- 开发工具
Python版本:3.6
相关模块:
import Scrapy from sinaweibo.items import SinaweiboItem import json import re import copy
- 分析网页
浏览发现使用的是使用Ajax渲染的网页,微博数据(https://m.weibo.cn/api/container/getIndex?containerid=102803_ctg1_5088-ctg1_5088&openApp=0&since_id=1)存储在json格式网页中,所以思路是先通过微博数据得到用户url(如下图),再来爬取后续内容。
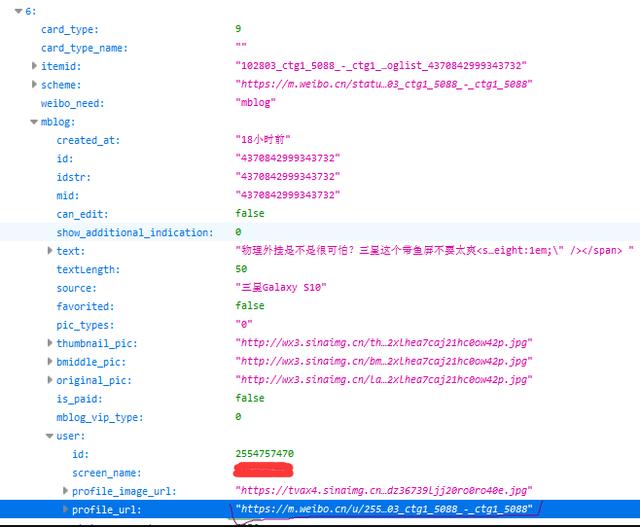
获取第一条微博数据
也是使用了Ajax渲染的网页,跟上面一样找到网页入口就行了。请求网址如下:

这样看网址的话毫无规律可言,简化后发现 https://m.weibo.cn/api/container/getIndex?containerid=1076032554757470就可以进入。而且containerid=107603(***)这里,括号里的数字刚好是用户的id号,因此我们可以通过这个来构造网页。
- 获取用户所在地区
用户所在地在其基本资料中,如下图

地址为:

同样进行简化得到:https://m.weibo.cn/api/container/getIndex?containerid=230283(***)-INFO其中括号里面是用户id号。
通过以上分析可知,获取用户的 id 号是本次爬取数据的关键,只需要用 id 构成网址,后面的爬取就相对简单了。下面是编程部分。
- 编程爬取
items.py定义爬虫字段
import scrapy ''' 遇到不懂的问题?Python学习交流群:821460695满足你的需求,资料都已经上传群文件,可以自行下载! ''' class SinaweiboItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: # name = scrapy.Field() name = scrapy.Field() #用户名 first_news = scrapy.Field() #首条微博 dates = scrapy.Field() #发布时间 zhuanzai = scrapy.Field() #转载数 comment = scrapy.Field() #评论数 agree = scrapy.Field() #点赞数 city = scrapy.Field() #所在地区
编写爬取代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy from sinaweibo.items import SinaweiboItem import json import re import copy ''' 遇到不懂的问题?Python学习交流群:821460695满足你的需求,资料都已经上传群文件,可以自行下载! ''' class WeibodiyuSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = 'weibodiyu' #爬虫名 allowed_domains = ['m.weibo.cn'] #只在该域名内爬取 start_urls = ['https://m.weibo.cn/api/container/getIndex?containerid=102803_ctg1_4188_-_ctg1_4188&openApp=0&since_id=1' ] def parse1(self, response): infos = json.loads(response.body) #将内容转为json对象 item = response.meta['item'] #利用meta方法传入item city = response.meta['city'] #传入城市 try: name = infos["data"]["cards"][0]["mblog"]["user"]["screen_name"] #爬取名字 first_news = re.findall('([\u4e00-\u9fa5] )', str(infos["data"]["cards"][0]["mblog"]["text"]), re.S) #爬取微博内容,使用正则去除一些杂项如网页代码 dates = infos["data"]["cards"][0]["mblog"]["created_at"] #发布时间 zhuanzai = infos["data"]["cards"][0]["mblog"]["reposts_count"] #转载数 comment = infos["data"]["cards"][0]["mblog"]["comments_count"] #评论数 agree = infos["data"]["cards"][0]["mblog"]["attitudes_count"] #点赞数 #将数据赋给item item['name'] = name item['first_news'] = first_news item['dates'] = dates item['zhuanzai'] = zhuanzai item['comment'] = comment item['agree'] = agree item['city'] = city return item #返回 except IndexError or KeyError: pass def parse2(self, response): #获取所在地区函数 infos = json.loads(response.body) try: item = response.meta['item'] #传入item city_cont = str(infos["data"]["cards"][1]["card_group"]) city = re.findall('card_type.*?所在地.*?item.*?:(.*?)}]', city_cont, re.S)[0].replace('\'', '').replace( ' ', '') #城市 item['city'] = city ids = response.meta['ids'] #传入id并赋给ids变量 n_url1 = 'https://m.weibo.cn/api/container/getIndex?&containerid=107603' ids yield scrapy.Request(n_url1, meta={'item': item, 'city': copy.deepcopy(city)}, callback=self.parse1) #执行完上述命令后的步骤 except IndexError or KeyError: pass def parse(self, response): datas = json.loads(response.body) item = SinaweiboItem() for i in range(0, 20): try: ids = str(datas["data"]["cards"][i]["mblog"]["user"]["id"]) #获取用户id n_url2 = 'https://m.weibo.cn/api/container/getIndex?containerid=230283{}_-_INFO'.format(ids) yield scrapy.Request(n_url2, meta={'item': item, 'ids': copy.deepcopy(ids)}, callback=self.parse2) #进入parse2函数执行命令 except IndexError or KeyError: pass social_urls = [ 'https://m.weibo.cn/api/container/getIndex?containerid=102803_ctg1_4188_-_ctg1_4188&openApp=0&since_id={}'.format( str(i)) for i in range(2, 100)] celebritys_urls = [ 'https://m.weibo.cn/api/container/getIndex?containerid=102803_ctg1_4288_-_ctg1_4288&openApp=0&since_id={}'.format( str(j)) for j in range(1, 100)] hots_urls = ['https://m.weibo.cn/api/container/getIndex?containerid=102803&openApp=0&since_id={}'.format(str(t)) for t in range(1, 100)] urls = celebritys_urls social_urls hots_urls #入口网址 for url in urls: yield scrapy.Request(url, callback=self.parse)
这里要注意 scrpay.Request 函数的meta参数,它是一个字典,用来进行参数传递,如上面代码所示,我想在parse2()函数中用到parse()函数中爬取的用户id,就需要进行设置,这里就不过多解释了,其实我也是处于摸着石头过河的理解程度,想深入了解的朋友可自行百度。
- 在setting.py配置爬虫
这次我只将内容导出到了csv文件中,方便后续筛选制作词云,如果爬取的数据较多的话,可以存储到数据库中。
BOT_NAME = 'sinaweibo' SPIDER_MODULES = ['sinaweibo.spiders'] NEWSPIDER_MODULE = 'sinaweibo.spiders' USER_AGENT: 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/73.0.3683.103 Safari/537.36' #消息头 DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 0.5 #延时0.5s # Crawl responsibly by identifying yourself (and your website) on the user-agent #USER_AGENT = 'sinaweibo ( http://www.yourdomain.com)' FEED_URI = 'file:C:/Users/lenovo/Desktop/weibo.csv' #存入文件位置 FEED_FORMAT = 'csv' #保存格式 ITEM_PIPELINES= {'sinaweibo.pipelines.SinaweiboPipeline': 300} #管道设置 # Obey robots.txt rules ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = False FEED_EXPORT_ENCODING = 'UTF8' #编码格式
本次没有下载图片及其他内容了,因此pipelines.py文件就没有编写内容了。爬取的部分数据如下:

到这里爬虫部分就结束了,本次爬取的内容也较为简单,下面的话就是使用其中的部分数据来生成词云。
- 词云制作
在文件中新建了一个 weibo_analysis.py 的文件,使用jieba库来进行分词,在此之前,需要先将所需数据提取出来,这里使用pandas就可以。
这部分程序很简单,就不废话了,直接上代码:
import csv import pandas as pd import jieba.analyse ''' 遇到不懂的问题?Python学习交流群:821460695满足你的需求,资料都已经上传群文件,可以自行下载! ''' def get_ciyun(city): #进行分词 tags=jieba.analyse.extract_tags(str(city),topK=100,withWeight=True) for item in tags: print(item[0] '\t' str(int(item[1]*1000))) need_citys = ['北京', '上海', '湖南', '四川', '广东'] beijing = [] shanghai = [] hunan = [] sichuan = [] gd = [] pd.set_option('expand_frame_repr', True) #可换行显示 pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None) #显示所有行 pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None) #显示所有列 df = pd.read_csv('C:\\Users\lenovo\Desktop\weibo.csv') #读取文件内容并转化为dataframes对象 contents = df['first_news'] #取微博内容 city = df['city'] #取城市 for i in range(len(city)): if need_citys[0] in city[i]: #判断并存入 beijing.append(contents[i]) elif need_citys[1] in city[i]: shanghai.append(contents[i]) elif need_citys[2] in city[i]: hunan.append(contents[i]) elif need_citys[3] in city[i]: sichuan.append(contents[i]) elif need_citys[4] in city[i]: gd.append(contents[i]) else: pass #输出 get_ciyun(beijing) print('-'*20) get_ciyun(shanghai) print('-'*20) get_ciyun(hunan) print('-'*20) get_ciyun(sichuan) print('-'*20) get_ciyun(gd)
本次是通过Tagul网站在制作词云,将上方输出的词频导入,选择好词云形状、字体(不支持中文可自行导入中文字体包)、颜色等点击可视化就能生成了,非常方便。
下面是我本次生成的词云图片:




Scrapy爬取新浪微博移动版用户首页微博
,




