https://github.com/jfeliu007/goplantuml/是一款工具可以解析golang源码,生成plantuml类图,它的原理是通过源码静态分析,提取结构体,接口,方法,包等属性,然后按照uml语法生成puml文件,效果如下。
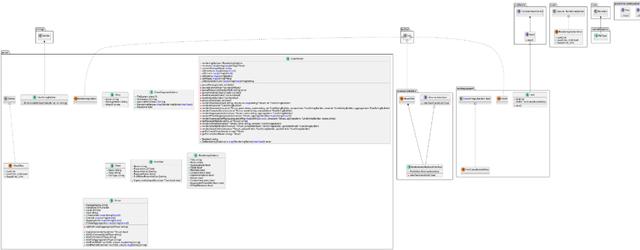
首先看下如何使用:
go get github.com/jfeliu007/goplantuml/parser
go install github.com/jfeliu007/goplantuml/cmd/goplantuml@latest
goplantuml $GOPATH/src/github.com/jfeliu007/goplantuml/parser > ClassDiagram.puml
// Generates a file ClassDiagram.puml with the previous specifications
然后我们就可以借助vscode plantuml插件生成上面的类图。熟悉完使用后我们来分析下它的源码。它的入口函数位于:cmd/goplantuml/main.go
func main() {
recursive := flag.bool("recursive", false, "walk all directories recursively")
ignore := flag.String("ignore", "", "comma separated list of folders to ignore")
showAggregations := flag.Bool("show-aggregations", false, "renders public aggregations even when -hide-connections is used (do not render by default)")
hideFields := flag.Bool("hide-fields", false, "hides fields")
renderingOptions := map[goplantuml.RenderingOption]interface{}{
legend, err := getLegend(renderingOptions)
dirs, err := getDirectories()
dirAbs, err := filepath.Abs(dir)
ignoredDirectories, err := getIgnoredDirectories(*ignore)
result, err := goplantuml.NewClassDiagram(dirs, ignoredDirectories, *recursive)
result.SetRenderingOptions(renderingOptions)
rendered := result.Render()
writer, err = os.Create(*output)
fmt.Fprint(writer, rendered)
解析完参数之后,将所有选项放入map,然后获取源码目录,以及忽略的目录,接着进行源码解析,提取生成plantuml需要的元数据信息后,调用渲染函数生成plantuml文件,最后输出。如果制定了标签,也会调用下面函数获取标签。
func getLegend(ro map[goplantuml.RenderingOption]interface{}) (string, error) {
它的核心解析函数定义在parser/class_parser.go
func NewClassDiagram(directoryPaths []string, ignoreDirectories []string, recursive bool) (*ClassParser, error) {
return NewClassDiagramWithOptions(options)
func NewClassDiagramWithOptions(options *ClassDiagramOptions) (*ClassParser, error) {
classParser := &ClassParser{
renderingOptions: &RenderingOptions{
structure: make(map[string]map[string]*struct),
allInterfaces: make(map[string]struct{}),
allStructs: make(map[string]Struct{}),
allImports: make(map[string]string),
allAliases: make(map[string]*Alias),
allRenamedStructs: make(map[string]map[string]string),
for _, dir := range options.IgnoredDirectories {
ignoreDirectoryMap[dir] = struct{}{}
for _, directoryPath := range options.Directories {
if options.Recursive {
err := afero.Walk(options.FileSystem, directoryPath, func(path string, info os.fileInfo, err error) error {
classParser.parseDirectory(path)
classParser.parseDirectory(path)
for s := range classParser.allStructs {
st := classParser.getStruct(s)
if st != nil {
for i := range classParser.allInterfaces {
inter := classParser.getStruct(i)
if st.ImplementsInterface(inter) {
st.AddToExtends(i)
}
}
}
}
classParser.SetRenderingOptions(options.RenderingOptions)
可以看到在准备完可选参数后,定义了一系列map,从名字到结构体信息映射,从名字到接口信息映射。用来存放提取的结构体信息,然后调用 afero.Walk,遍历所有目录和子目录。完成需要信息的提取。该函数是著名的spf13定义的一个文件接口包的一个函数:github.com/spf13/afero
在每个目录内都会调用解析函数进行解析,解析函数如下:
func (p *ClassParser) parseDirectory(directoryPath string) error {
fs := token.NewFileSet()
result, err := parser.ParseDir(fs, directoryPath, nil, 0)
for _, v := range result {
p.parsePackage(v)
它调用了golang源码的解析器,解析每个目录下的.go文件,返回包名到抽象语法树的映射。
func ParseDir(fset *token.FileSet, path string, filter func(fs.FileInfo) bool, mode Mode) (pkgs map[string]*ast.Package, first error) {
得到抽象语法树以后,就会遍历所有抽象语法树,解析每个包内的信息。
func (p *ClassParser) parsePackage(node ast.Node) {
pack := node.(*ast.Package)
p.currentPackageName = pack.Name
for fileName := range pack.Files {
sortedFiles = append(sortedFiles, fileName)
for _, fileName := range sortedFiles {
if !strings.HasSuffix(fileName, "_test.go") {
f := pack.Files[fileName]
for _, d := range f.Imports {
p.parseImports(d)
}
for _, d := range f.Decls {
p.parseFiledeclarations(d)
}
}
}
在每个包内依次递归解析它的下一层结构的信息:
func (p *ClassParser) parseImports(impt *ast.ImportSpec) {
p.allImports[impt.Name.Name] = s
解析过程中,提取了两类信息:
func (p *ClassParser) parseFileDeclarations(node ast.Decl) {
switch decl := node.(type) {
case *ast.GenDecl:
p.handleGenDecl(decl)
case *ast.FuncDecl:
p.handleFuncDecl(decl)
}
其中GenDecl包括下面四类信息:
// token.IMPORT *ImportSpec
// token.CONST *ValueSpec
// token.TYPE *typeSpec
// token.VAR *ValueSpec
func (p *ClassParser) handleGenDecl(decl *ast.GenDecl) {
for _, spec := range decl.Specs {
p.processSpec(spec)
}
对每个类型的内部每一部分也会进行处理:
func (p *ClassParser) processSpec(spec ast.Spec) {
switch v := spec.(type) {
case *ast.TypeSpec:
typeName = v.Name.Name
switch c := v.Type.(type) {
case *ast.StructType:
declarationType = "class"
handleGenDecStructType(p, typeName, c)
case *ast.InterfaceType:
declarationType = "interface"
handleGenDecInterfaceType(p, typeName, c)
default:
basicType, _ := getFieldType(getBasicType(c), p.allImports)
aliasType, _ := getFieldType(c, p.allImports)
aliasType = replacePackageConstant(aliasType, "")
if !isPrimitiveString(typeName) {
typeName = fmt.Sprintf("%s.%s", p.currentPackageName, typeName)
}
packageName := p.currentPackageName
if isPrimitiveString(basicType) {
packageName = builtinPackageName
}
alias = getNewAlias(fmt.Sprintf("%s.%s", packageName, aliasType), p.currentPackageName, typeName)
}
default:
p.getOrCreateStruct(typeName).Type = declarationType
switch declarationType {
case "interface":
p.allInterfaces[fullName] = struct{}{}
case "class":
p.allStructs[fullName] = struct{}{}
case "alias":
p.allAliases[typeName] = alias
if strings.Count(alias.Name, ".") > 1 {
pack := strings.SplitN(alias.Name, ".", 2)
if _, ok := p.allRenamedStructs[pack[0]]; !ok {
p.allRenamedStructs[pack[0]] = map[string]string{}
}
renamedClass := generateRenamedStructName(pack[1])
p.allRenamedStructs[pack[0]][renamedClass] = pack[1]
}
}
对于结构体类型,会纯粹在Struct的结构体里:
func handleGenDecStructType(p *ClassParser, typeName string, c *ast.StructType) {
for _, f := range c.Fields.List {
p.getOrCreateStruct(typeName).AddField(f, p.allImports)
}
}
func (p *ClassParser) getOrCreateStruct(name string) *Struct {
result = &Struct{
PackageName: p.currentPackageName,
Functions: make([]*Function, 0),
Fields: make([]*Field, 0),
Type: "",
Composition: make(map[string]struct{}, 0),
Extends: make(map[string]struct{}, 0),
Aggregations: make(map[string]struct{}, 0),
privateAggregations: make(map[string]struct{}, 0),
}
interface的处理是类似的:
func handleGenDecInterfaceType(p *ClassParser, typeName string, c *ast.InterfaceType) {
for _, f := range c.Methods.List {
switch t := f.Type.(type) {
case *ast.FuncType:
p.getOrCreateStruct(typeName).AddMethod(f, p.allImports)
break
case *ast.Ident:
f, _ := getFieldType(t, p.allImports)
st := p.getOrCreateStruct(typeName)
f = replacePackageConstant(f, st.PackageName)
st.AddToComposition(f)
break
}
}
函数的处理:
func (p *ClassParser) handleFuncDecl(decl *ast.FuncDecl) {
theType, _ := getFieldType(decl.Recv.List[0].Type, p.allImports)
theType = replacePackageConstant(theType, "")
structure := p.getOrCreateStruct(theType)
structure.AddMethod(&ast.Field{
Names: []*ast.Ident{decl.Name},
Doc: decl.Doc,
Type: decl.Type,
Tag: nil,
Comment: nil,
}, p.allImports)
func (p *ClassParser) getStruct(structName string) *Struct {
解析完成后设置渲染选项,为最终渲染成plantuml做准备:
func (p *ClassParser) SetRenderingOptions(ro map[RenderingOption]interface{}) error {
for option, val := range ro {
switch option {
case RenderAggregations:
其中解析过程中用到了go语言本性的包
"go/ast"
"go/parser"
"go/token"
渲染的过程,就是将解析得到的元数据信息,渲染成plantuml语法
func (p *ClassParser) Render() string {
str.WriteLineWithDepth(0, "@startuml")
str.WriteLineWithDepth(0, fmt.Sprintf(`title %s`, p.renderingOptions.Title))
str.WriteLineWithDepth(0, "legend")
str.WriteLineWithDepth(0, note)
str.WriteLineWithDepth(0, "end legend")
for pack := range p.structure {
packages = append(packages, pack)
for _, pack := range packages {
structures := p.structure[pack]
p.renderStructures(pack, structures, str)
if p.renderingOptions.Aliases {
p.renderAliases(str)
str.WriteLineWithDepth(0, "@enduml")
对于每个具体结构也是递归进行渲染的和解析过程是类似的
func (p *ClassParser) renderStructures(pack string, structures map[string]*Struct, str *LineStringBuilder) {
str.WriteLineWithDepth(0, fmt.Sprintf(`namespace %s {`, pack))
for _, name := range names {
structure := structures[name]
p.renderStructure(structure, pack, name, str, composition, extends, aggregations)
for _, tempName := range orderedRenamedStructs {
name := p.allRenamedStructs[pack][tempName]
str.WriteLineWithDepth(1, fmt.Sprintf(`class "%s" as %s {`, name, tempName))
if p.renderingOptions.Compositions {
str.WriteLineWithDepth(0, composition.String())
}
if p.renderingOptions.Implementations {
str.WriteLineWithDepth(0, extends.String())
}
if p.renderingOptions.Aggregations {
str.WriteLineWithDepth(0, aggregations.String())
}
结构体的渲染
func (p *ClassParser) renderStructure(structure *Struct, pack string, name string, str *LineStringBuilder, composition *LineStringBuilder, extends *LineStringBuilder, aggregations *LineStringBuilder) {
switch structure.Type {
case "class":
sType = "<< (S,Aquamarine) >>"
case "alias":
sType = "<< (T, #FF7700) >> "
renderStructureType = "class"
}
p.renderStructFields(structure, privateFields, publicFields)
p.renderStructMethods(structure, privateMethods, publicMethods)
p.renderCompositions(structure, name, composition)
p.renderExtends(structure, name, extends)
p.renderAggregations(structure, name, aggregations)
其中渲染的目标就是string.Builder
type LineStringBuilder struct {
strings.Builder
}
如果有别名会解析到:parser/alias.go
type Alias struct {
Name string
PackageName string
AliasOf string
}
结构体被解析到:parser/struct.go
type Struct struct {
PackageName string
Functions []*Function
Fields []*Field
Type string
Composition map[string]struct{}
Extends map[string]struct{}
Aggregations map[string]struct{}
PrivateAggregations map[string]struct{}
}
判断一个结构体是否实现了接口,就是判断结构体的方法签名和接口所有的函数列表是否一致
func (st *Struct) ImplementsInterface(inter *Struct) bool {
for _, f1 := range inter.Functions {
for _, f2 := range st.Functions {
if f1.SignturesAreEqual(f2) {
func (st *Struct) AddToExtends(fType string) {
st.Extends[fType] = struct{}{}
函数的信息描述位于:parser/function.go
type Function struct {
Name string
Parameters []*Field
ReturnValues []string
PackageName string
FullNameReturnValues []string
}
判断签名是否一致,会判断输入和返回信息:
func (f *Function) SignturesAreEqual(function *Function) bool {
result = result && (len(f.Parameters) == len(function.Parameters))
结构体字段信息描述位于:parser/field.go
type Field struct {
Name string
Type string
FullType string
}
总结起来,这类工具大同小异,都是解析源码获取元数据信息,然后将元数据信息翻译成目标语言或者协议
,




