名词(表示人和事物名称的词):
专有名词:特定的人、地方、机构等专有的名称。第一个字母通常要大写。
e.g. Jim Green,New York, Bank of China,PekingUniversity.
星期、月份、节日、学科、报刊名也是专有名词。
普通名词:
1)个体名词—表示某类人或东西中的个体,如:student,desk
2)集体名词—表示若干个体组成的集合体,如:class,family
3)物质名词—表示无法分为个体的物质名称,如:water,rice,sand,hair
4)抽象名词—表示情感,状态,品质等抽象名称,如:love,carelessness
个体名词和集体名词多数可以用数目来计算,称为可数名词,有单、复数形式;
物质名词和抽象名词通常无法用数目计算,称为不可数名词,一般只有一种形式。
英语语法中,只有可数名词才有复数形式。名词有两种数的形式:
1)单数(表示一个人或事物);
2)复数(表示多于一个的人或数)。

名词复数形式的构成:
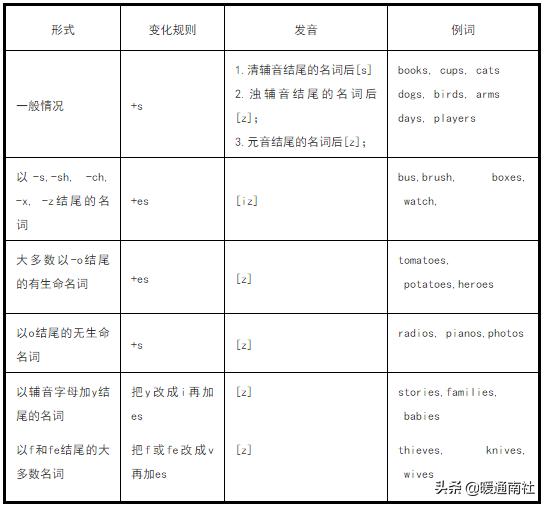
不规则名词的复数:
1.由元音字母的变化构成:
man-men, tooth-teeth, foot-feet,mouse-mice, woman-women
2.有些名词的复数形式与单数的形式一样:sheep,deer,fish(但也可以是fishes)
有些名词变成复数时加-en:child-children,ox-oxen
例:
人称代词和物主代词:

例如:
1._He_ (他) ismy brother.
2. I had a letter from _her_ (她).
3. It’s all right; it’s only __me__(我).
4. Today __we__(我们)went in _our_(我们的) car; tomorrow __we__(我们) are going in __their__(他们的).
5. __I__(我)lend __my_(我的) books gladly to _my__(我的) friends and to __yours__ (你的).
6. Can you help _me__ (我)with __my_ (我的) English.
7. When __you__(你) goto see __your__ (你的) father, please take thesebooks to __him__(他).
8. __They__(他们)found __it__(它) difficult to learn German.
双重所有格:
所有格的形式:
单数人称名词末尾加’s child-child’s
以-s结尾的单数人称名词末尾加’s waitress-waitress’s
不规则的复数人称名词末尾加’s children-children’s
以-s结尾的复数人称名词末尾加’ girls-girls’
以-s结尾的一些人名末尾加’s James-James’s
’s结构也可以用于“of”结构之后,如:a friend of
my father’s, 出现这种情况是因为在一个名词前通常只用一个限定词,又如:this son of mine, a friend of yours, a cousin of hers等等。
Isn’t Frank a friend of yours?
That silly uncle of Tom’s has told methe same.
Joke five times.
下列情况一般用“of”结构:
1.东西(没有现成的复合名词时): the book of the film
2.东西的一部分:the bottom of the box
3.抽象的概念:the price of success
4.当of短语中的名词被另一个短语或从句修饰时:
Can’t you look at the book of the boybehind you?
冠词:
1.不定冠词a,an→只能用于单数可数名词之前。
2.定冠词the:单数可数名词;复数可数名词;不可数名词。
3.零冠词:名词前可不用冠词。
1. Do you like playing __/__volleyball here?
Yes. Look! I have __a__volleyball.
2. Can you see _an_ eraser on _the_desk? Yes, whose is it?
动词:
动词主要表示动作,其次表示状态或性质,有时态、语态、语气等形式的变化。
小学阶段所涉及的动词主要有:实义动词、be动词、情态动词can,must等。
Be动词:am,is,are;was,were,例:
1. He __is___ very good atEnglish.
2. My father and I __are__ goingto Beijing next month.
3. _Were_ you on duty the daybefore yesterday?
4. Mr. King _was__ in London twoweeks ago.
5. There _are__ many kinds ofanimals in the zoo.
6. What _was__ the dateyesterday?
7. Look! A little girl __is__flying a kite.
8. Who __was__ not at schoollast Monday?
9. I _am__ not a nurse. I workas a doctor.
动词的时态:
小学阶段所学的时态有:
1.一般现在时:work/works
2.现在进行时:am/is/are working
3.一般过去时:worked
4.一般将来时:am/is/are going to work/willwork
动词过去式变化规则:
1.一般在动词末尾加-ed,如:work-worked
2.结尾是e加d,如:live--lived
3.末尾只有一个元音字母和一个辅音字母的重读闭音节,应双写末尾的辅音字母,再加-如:stop-stopped
4.以“辅音字母 y”结尾的,变y为i,再加-ed,如:study-studied
例:
Peter __plays__ (play)basketball twice a week.
Look! The lazy cat __is sleeping__(sleep) in the sofa.
Are_you _goingto see_ (see) a film tomorrow morning?
I didn’t feel_ (not feel)very well yesterday.
介词:
介词在句子中表示名词或代词等与其他词之间的关系。不能单独作句子成分,常位于名词或代词(或与之相当的其他词类、短语、从句)前面构成介词短语。介词后面的成分作介词的宾语。
方位介词:in, on, at, under, to,behind, beside, near, before, in front of, next to, between
时间介词:in, on, at, after,before, from…to, past, between
其它:of, by, with, into, out of,for
Look _at_ the picture. It'spicture_of_ my school.
_In_ _front_ _of_the house,there are many trees.
Miss Li is our class teacher. She comes_to_ school early every morning. She comes _by_bicycle. Then shedoes morning exercises _with_us. She likes sports. Tomorrow is herbirthday. We will make a card _for_ her. We love her very much.
形容词和副词:
形容词是用来描写或修饰名词(或代词)的词。
1.He is a good student.
2.The film is very interesting.
3.There is something wrong withthe bike.
4.Lucy is older than Helen.
副词是用来修饰动词、形容词、其他副词以及全句的词。
1.The problem is very difficult.
2.He wrote the letters carefully.
形容词和副词的比较级和最高级:

例:
Shanghai is _larger_than Beijing. It is _the largest_cityin our country. (large)
Tom, John and I bought a computer eachlast week. John’s computer is much _moreexpensive _ than Tom’s and mine. It is the most expensive of thethree. (expensive)
There be的结构:
There be表示“存在有”,即当我们告诉某人某事存在(或不存在)常用这种结构。其中there是引导词,本身无词义;be为谓语动词,后面跟的是名词,也就是主语,也就是说there be结构的运用也就是倒装的具体运用。其真正的主语在there be 之后。
肯定句:There is/was a …
There are/were …
一般疑问句:Is/Was there …?
Yes, there is/was. No, there isn’t/was.
Are there…?
Yes, there are/were.
No, there aren’t/weren’t.
否定句:There isn’t/wasn’t …
There aren’t/weren’t…
Some 和 any:
一般情况下,some用于肯定句中,any用于否定句中。如:
There is some milk in the bottle.
There aren’t any pictures on the wall.
Is there anything new in today’snewspaper?
Be动词与后面所跟名词的就近原则:
There is a pen and two pencils in thebox.
There are some students and a teacherin the classroom.
There is _an old woman in thecar.
There is some __bread _ on the plate.
_Are there _ anyflowers on both sides of the street?
“Wh”的疑问句:
What:
1) What’s this/that? 2) What’s your name?
3) What are you doing? 4) What do you like/need?
5) What did you do? 6) What is his job?
7) What do you usually do at theweekends?
How:
1) How are you?
2) How old are you?
3) How do we go to the park?
4) How many apples can you see?
5) How much are they?
Who:
Who is that?
Who’s that boy in/with…?
Whose:
1)Whose is this bike?
2)Whose bike is this?
3)Whose bag is bigger, yours or mine?
Which:
1) Which one?
2) Which is longer, yours or mine?
3) Which season do you like best?
Where:
1) Where is the book?
2) Where are you from?
Why—Why?

例:
1.Tom visits the Science Museumevery year.
What does Tom visit every year?
2.The building near the factoryis the People’s hospital.
Which building is the People’shospital?
3.It’s cloudy today.
What’s the weather like today?
4.I usually take No. 4 bus towork.
Which bus do you usually take to work?
5.Uncle Wang feels better now.
How does Uncle Wang feel now?
6.I go to work at eight.
What time do you go to work?
7.They are cleaning their classroomnow.
What are they doing now?
祈使句:
表示请求或命令别人做某事或不要做某事。
肯定祈使句一定是以动词原形开头(有时有please),否定的祈使句一定是don’t加动词原形开头(有时有please)。
把祈使句改为否定句只需在动词前加don’t即可。
来源于互联网学习资料整合。暖通南社整理编辑。
,




