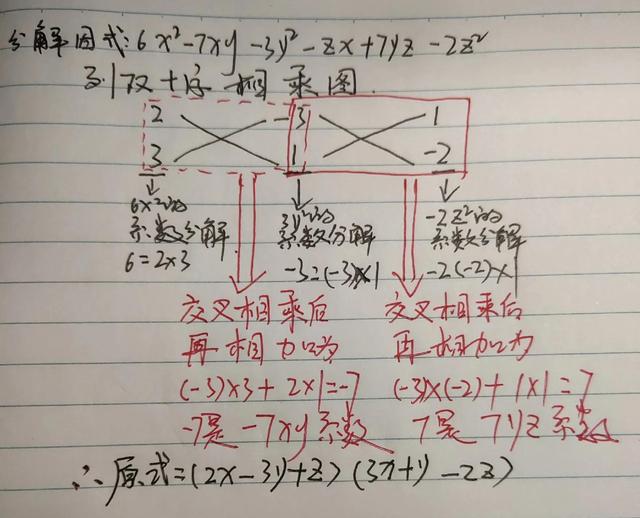
A-level economics revision guides and question banks covering labour markets, supply and demand, market structure and all core economics a-level topics.
以下内容我们会持续更新:

今天带给大家Alevel经济笔记是:
第三章:Elasticities—
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand Formulae;
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand
A definition and the formulaIf you understand the concept of price elasticity of demand, then it is fairly easy to grasp cross price elasticity of demand.
The issue is still how responsive demand is to a given price change, the difference here is that one is measuring the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of one good with respect to a given price change in a different good, ceteris paribus.
如果你理解了需求价格弹性的概念,那么理解需求的交叉价格弹性是相当容易的。问题仍然是需求对给定价格变化的响应程度,这里的区别在于衡量一种商品的需求量相对于另一种商品的给定价格变化的响应性,其他条件不变。
As you can see, the formula used to calculate the cross price elasticity of demand is basically the same as the one used to calculate the price elasticity of demand, except for the distinction between good A and good B:
可以看到,计算需求交叉价格弹性的公式与计算需求价格弹性的公式基本相同,除了商品A和商品B的区别:

Where:
EY = The income elasticity of demand
Δ = 'change in'
Qd = Quantity demanded
Y = Real income
Substitute, complement and independent goods替代品、互补品和独立品
The cross price elasticity of demand is useful for economists because it tells you whether two goods (A and B) are substitutes, complements or even unrelated.
Think about this example:
需求的交叉价格弹性对经济学家很有用,因为它可以告诉您两种商品(A 和 B)是否是替代品、互补品,甚至是不相关的。想想这个例子:
Tea and coffee are substitutes.
Let's say that tea is good A and coffee is good B. If the price of coffee falls by, say, 10% ceteris paribus, then one would expect coffee to become relatively more popular at the expense of the demand for tea.
The demand for tea might fall by, say, 5%. Using the formula above, we can calculate the cross price elasticity:
茶和咖啡是替代品。假设茶是好的 A,咖啡是好的 B。如果咖啡的价格下降,比如说,在其他条件不变的情况下下降 10%,那么人们会期望咖啡变得相对更受欢迎,但会牺牲对茶的需求。对茶的需求可能会下降 5%。使用上面的公式,我们可以计算交叉价格弹性:

Briefly, the price of coffee falls, so the demand for tea falls. This is a positive relationship, as is true for all pairs of goods that are substitutes.
If the cross price elasticity of demand is positive then the two goods in question will be substitutes.
简而言之,咖啡价格下跌,因此对茶的需求下降。这是一种正向关系,对于所有可替代的商品对都是如此。如果需求的交叉价格弹性为正,那么这两种商品将是替代品。
Tea and sugar are complements. Sugar is a complement to a cup of tea (for some people, anyway!).
Assume that sugar is good A and tea is good B. If the price of tea fell by, say, 10% ceteris paribus, then one would expect the demand for tea to rise.
This should cause the demand for sugar to rise, although not everyone has sugar in their tea, and if they do the quantities are not exactly massive, so the rise in demand for sugar is likely to be a lot smaller than the rise in demand for tea. Let's say that the demand for sugar rises by 2%. Using the formula, we have:
茶和糖是互补的。糖是一杯茶的补充(对某些人来说,无论如何!)。假设糖是好的 A,茶是好的 B。如果茶的价格下降,比如说,在其他条件不变的情况下下降 10%,那么人们会预期对茶的需求会上升。这应该会导致对糖的需求上升,尽管不是每个人的茶中都有糖,而且如果他们这样做,数量也不是很大,所以对糖的需求增长可能比对糖的需求增长要小得多。茶。假设对糖的需求增加了 2%。使用公式,我们有:

Put briefly, the price of tea falls, so the demand for sugar rises. This is a negative relationship, as is true for all pairs of goods that are complements.
If the cross price elasticity of demand is negative then the two goods in question will be complements.
简而言之,茶叶价格下跌,因此对糖的需求增加。这是一种负关系,对于所有互补的商品对都是如此。如果需求的交叉价格弹性为负,那么这两种商品将是互补品。
What will happen to the demand for sugar when the price of cinema admissions changes, ceteris paribus? Absolutely nothing, I should think. The two goods are completely unrelated. Using the formula:
在其他条件不变的情况下,当电影院门票价格发生变化时,糖的需求会发生什么变化?绝对没有,我应该想。这两种商品完全不相关。使用公式:

If the cross price elasticity of demand is zero then the two goods in question will be totally unrelated (or independent).
如果需求的交叉价格弹性为零,那么所讨论的两种商品将完全不相关(或独立)。
Finally, note that the higher the value of the cross price elasticity, the stronger the relationship between the two goods in question, whether they be substitutes of complements.
The nearer the figure is to zero, the more likely that the two goods are unrelated.
最后,请注意交叉价格弹性的值越高,这两种商品之间的关系越强,无论它们是否是互补品的替代品。该数字越接近于零,两种商品不相关的可能性就越大。
今天的Alevel经济笔记就更新到这里,如果大家对Alevel经济学感兴趣可以关注我们,
关于Alevel经济笔记第三章:Elasticities后续的更新计划如下: