“分布式锁”是用来解决分布式应用中“并发冲突”的一种常用手段,实现方式一般有基于zookeeper及基于redis二种。
这里我们分析下基于redis得场景和实现。
单节点部署场景- 举例说明,系统A和系统B是两个部署在不同节点的相同应用(集群部署),这时客户端请求传来,两个系统都受到了请求,并且该请求是对数据表进行插入操作,如果这个时候不加锁来控制,可能会导致数据库新增两条记录,这时系统也不能允许的,由于是在不同应用内,在单个应用内加JVM级别的锁,另一个应用是感知不到的,这时需要用到分布式锁。
- 接下来我们看看这种场景如何实现安全的分布式锁,由于是单节点部署场景,我们可以用setnx命令,以请求的唯一主键作为key,由于该操作是原子操作,当系统A设值成功后,系统B是无法设置成功的, 这时A就可以进行查询并插入操作,操作数据库完成后,删除key,此时系统B才能设值成功,但是由于查询到数据库有记录,所以并不会插入数据,这样就解决了该问题。但是这里会有个问题,如果redis挂机了,这里的锁不是永远都不释放了吗, 所以为了解决这个问题,redis提供了set命令,可传入超时时间的,那么在指定的时间范围内,如果没有释放锁,则该锁自动过期。如果执行时间超过超时时间呢,比如系统A还未执行完任务,就释放了锁,系统B接着执行任务,这时,系统A执行完了,把锁删掉(此时删除的时系统B获取的锁)。方案一: 为了避免这种情况,在del锁之前可以做一个判断,验证key对应的value是不是自己线程的ID.如果要考虑原子性问题,可以使用Lua脚本来实现,保证验证和删除的原子性。方案二:我们可以让获得锁的线程开启一个守护线程,用来给快要过期的锁加长超时时间。当系统A中的线程执行完任务,再显式关掉守护线程。
具体到业务场景中,我们要考虑二种情况:
一、抢不到锁的请求,允许丢弃(即:忽略)
比如:一些不是很重要的场景,比如“监控数据持续上报”,某一篇文章的“已读/未读”标识位更新,对于同一个id,如果并发的请求同时到达,只要有一个请求处理成功,就算成功。
用活动图表示如下:

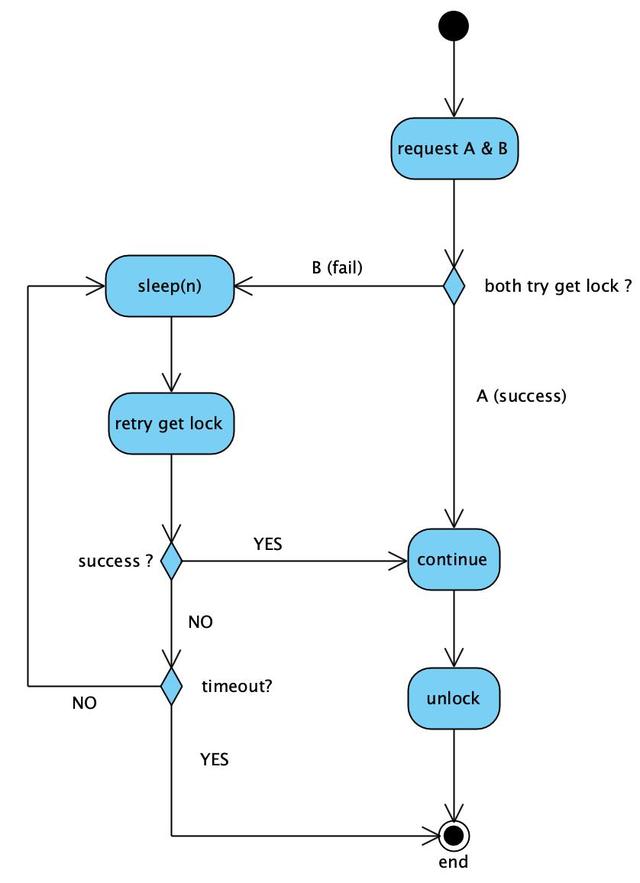
二、并发请求,不论哪一条都必须要处理的场景(即:不允许丢数据)
比如:一个订单,客户正在前台修改地址,管理员在后台同时修改备注。地址和备注字段的修改,都必须正确更新,这二个请求同时到达的话,如果不借助db的事务,很容易造成行锁竞争,但用事务的话,db的性能显然比不上redis轻量。
解决思路:A,B二个请求,谁先抢到分布式锁(假设A先抢到锁),谁先处理,抢不到的那个(即:B),在一旁不停等待重试,重试期间一旦发现获取锁成功,即表示A已经处理完,把锁释放了。这时B就可以继续处理了。
但有二点要注意:
a、需要设置等待重试的最长时间,否则如果A处理过程中有bug,一直卡死,或者未能正确释放锁,B就一直会等待重试,但是又永远拿不到锁。
b、等待最长时间,必须小于锁的过期时间。否则,假设锁2秒过期自动释放,但是A还没处理完(即:A的处理时间大于2秒),这时锁会因为redis key过期“提前”误释放,B重试时拿到锁,造成A,B同时处理。(注:可能有同学会说,不设置锁的过期时间,不就完了么?理论上讲,确实可以这么做,但是如果业务代码有bug,导致处理完后没有unlock,或者根本忘记了unlock,分布式锁就会一直无法释放。所以综合考虑,给分布式锁加一个“保底”的过期时间,让其始终有机会自动释放,更为靠谱)
用活动图表示如下:
写了一个简单的工具类:
package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.Redisdistributionlock;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 利用redis获取分布式锁
*
* @author 菩提树下的杨过
* @blog http://yjmyzz.cnblogs.com/
*/
public class RedisLock {
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
/**
* simple lock尝试获取锅的次数
*/
private int retryCount = 3;
/**
* 每次尝试获取锁的重试间隔毫秒数
*/
private int waitIntervalInMS = 100;
public RedisLock(StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
}
/**
* 利用redis获取分布式锁(未获取锁的请求,允许丢弃!)
*
* @param redisKey 锁的key值
* @param expireInSecond 锁的自动释放时间(秒)
* @return
* @throws DistributionLockException
*/
public String simpleLock(final String redisKey, final int expireInSecond) throws DistributionLockException {
String lockValue = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
boolean flag = false;
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(redisKey)) {
throw new DistributionLockException("key is empty!");
}
if (expireInSecond <= 0) {
throw new DistributionLockException("expireInSecond must be bigger than 0");
}
try {
for (int i = 0; i < retryCount; i ) {
boolean success = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(redisKey, lockValue, expireInSecond, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (success) {
flag = true;
break;
}
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(waitIntervalInMS);
} catch (Exception ignore) {
logger.warn("redis lock fail: " ignore.getMessage());
}
}
if (!flag) {
throw new DistributionLockException(Thread.currentThread().getName() " cannot acquire lock now ...");
}
return lockValue;
} catch (DistributionLockException be) {
throw be;
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("get redis lock error, exception: " e.getMessage());
throw e;
}
}
/**
* 利用redis获取分布式锁(未获取锁的请求,将在timeoutSecond时间范围内,一直等待重试)
*
* @param redisKey 锁的key值
* @param expireInSecond 锁的自动释放时间(秒)
* @param timeoutSecond 未获取到锁的请求,尝试重试的最久等待时间(秒)
* @return
* @throws DistributionLockException
*/
public String lock(final String redisKey, final int expireInSecond, final int timeoutSecond) throws DistributionLockException {
String lockValue = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
boolean flag = false;
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(redisKey)) {
throw new DistributionLockException("key is empty!");
}
if (expireInSecond <= 0) {
throw new DistributionLockException("expireInSecond must be greater than 0");
}
if (timeoutSecond <= 0) {
throw new DistributionLockException("timeoutSecond must be greater than 0");
}
if (timeoutSecond >= expireInSecond) {
throw new DistributionLockException("timeoutSecond must be less than expireInSecond");
}
try {
long timeoutAt = System.currentTimeMillis() timeoutSecond * 1000;
while (true) {
boolean success = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(redisKey, lockValue, expireInSecond, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (success) {
flag = true;
break;
}
if (System.currentTimeMillis() >= timeoutAt) {
break;
}
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(waitIntervalInMS);
} catch (Exception ignore) {
logger.warn("redis lock fail: " ignore.getMessage());
}
}
if (!flag) {
throw new DistributionLockException(Thread.currentThread().getName() " cannot acquire lock now ...");
}
return lockValue;
} catch (DistributionLockException be) {
throw be;
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("get redis lock error, exception: " e.getMessage());
throw e;
}
}
/**
* 锁释放
*
* @param redisKey
* @param lockValue
*/
public void unlock(final String redisKey, final String lockValue) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(redisKey)) {
return;
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(lockValue)) {
return;
}
try {
String currLockVal = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(redisKey);
if (currLockVal != null && currLockVal.equals(lockValue)) {
boolean result = redisTemplate.delete(redisKey);
if (!result) {
logger.warn(Thread.currentThread().getName() " unlock redis lock fail");
} else {
logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() " unlock redis lock:" redisKey " successfully!");
}
}
} catch (Exception je) {
logger.warn(Thread.currentThread().getName() " unlock redis lock error:" je.getMessage());
}
}
}
然后写个spring-boot来测试一下:
package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.redisdistributionlock;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@SpringBootApplication
public class RedisDistributionLockApplication {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RedisDistributionLockApplication.class);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(RedisDistributionLockApplication.class, args);
//初始化
StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(StringRedisTemplate.class);
RedisLock redisLock = new RedisLock(redisTemplate);
String lockKey = "lock:test";
CountDownLatch start = new CountDownLatch(1);
CountDownLatch threadsLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);
final int lockExpireSecond = 5;
final int timeoutSecond = 3;
Runnable lockRunnable = () -> {
String lockValue = "";
try {
//等待发令枪响,防止线程抢跑
start.await();
//允许丢数据的简单锁示例
lockValue = redisLock.simpleLock(lockKey, lockExpireSecond);
//不允许丢数据的分布式锁示例
//lockValue = redisLock.lock(lockKey, lockExpireSecond, timeoutSecond);
//停一会儿,故意让后面的线程抢不到锁
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
logger.info(String.format("%s get lock successfully, value:%s", Thread.currentThread().getName(), lockValue));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
redisLock.unlock(lockKey, lockValue);
//执行完后,计数减1
threadsLatch.countDown();
}
};
Thread t1 = new Thread(lockRunnable, "T1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(lockRunnable, "T2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
//预备:开始!
start.countDown();
//等待所有线程跑完
threadsLatch.await();
logger.info("======>done!!!");
}
}
用2个线程模拟并发场景,跑起来后,输出如下:

可以看到T2线程没抢到锁,直接抛出了预期的异常。
把44行的注释打开,即:换成不允许丢数据的模式,再跑一下:

可以看到,T1先抢到锁,然后经过2秒的处理后,锁释放,这时T2重试拿到了锁,继续处理,最终释放。
,