是Microsoft Windows中的一个重要的数据库,用于存储系统和应用程序的设置信息。
- [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT]==[HKCR]系统文件信息
记录Windows操作系统中所有数据文件的格式和关联信息,主要记录不同文件的文件名后缀和与之对应的应用程序。其下子键可分为两类:一类是已经注册的各类文件的扩展名,这类子键前面都有一个“.”;另一类是各类文件类型有关信息。
- 官方已做如下建议:
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT为早期版本的 Windows 设计的程序提供此合并视图。 若要更改交互式用户的设置,必须更改 HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Classes ,而不是HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT。 若要更改默认设置,必须更改 HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes 。 如果将信息写入注册表项下的HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT,系统会将信息存储在 HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes 下。 如果将值写入 HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT 下的项,并且该项键值已存在,则系统会将信息存储在 HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Classes ,而不是存储在 HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes 。
- [HKEY_CURRENT_USER]==[HKCU]当前用户数据
当前登录用户的用户配置文件信息。
- [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE]==[HKLM]系统核心数据
当前计算机的配置数据,包括所安装的硬件以及软件的设置。
- [HKEY_USERS]==[HKU]用户数据
默认用户的信息(Default子键)和所有以前登录用户的信息。
- [HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG]当前配置数据
是HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE中的一部分,其中存放的是计算机当前设置。
2. 修改注册表的方法注:切记修改注册表前,一定要备份。
- regedit注册表编辑器
在dos窗口或powershell窗口,输入regedit回车,出现注册表编辑器界面。
- reg命令
在dos窗口或powershell窗口,输入reg /?查看帮助。
- powershell(pwsh)
在powershell窗口,输入help item查看相关帮助。
- 编写reg注册表脚本文件
扩展名为.reg的文本文件,有固定的格式要求。
一般少量零星的注册表操作, 直接使用regedit或reg过powershell操作方便; 为实现某个功能需对注册表进行有关联的操作,编写.reg文件比较合适。
3. 数据类型对照表

注:
- reg_multi_sz和reg_expand_sz不常用, 若必须使用,建议用regedit、reg、powershell操作注册表
- 键值支持环境变量(%var%)和位置参数(%n)
- 特殊字符(")需转义(\), 如:""%SystemRoot%\system32\notepad.exe " "%1""
修改注册表的项键值,达到设置环境变量的目的。
4.1. 环境变量所在注册表位置- 用户变量所在位置:HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment
- 系统变量所在位置:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Session Manager\Environment
按win r后,输入regedit回车,出现注册表编辑器界面,可以直接进行增删改查、导出、导入等操作。
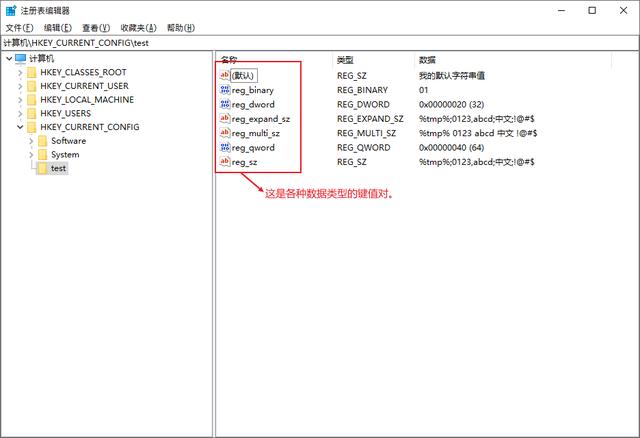
设置java环境变量为例,编写bat或cmd或ps1文件。
- reg命令
:: env_java.bat or env_java.cmd
:: reg /?
:: 临时变量
set hkcu_env_root="HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment"
set hklm_env_root="HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Session Manager\Environment"
reg query %hkcu_env_root%
reg query %hklm_env_root%\CLASSPATH
:: 设置系统环境变量
reg add %hklm_env_root% /v JAVA_HOME /t REG_SZ /d "D:\\java\\jdk-15" /f
reg add %hklm_env_root% /v CLASSPATH /t REG_SZ /d .;^%JAVA_HOME^%\lib /f
:: 注意: 在扩充字符串中使用插入符号 ( ^ ) 保留%
: reg add %hklm_env_root% /v Path /t REG_EXPAND_SZ /d ^%JAVA_HOME^%\bin;%Path% /f
:: %var%将被替换为实际值
reg add %hklm_env_root% /v Path /t REG_EXPAND_SZ /d "%JAVA_HOME%\bin;%Path%" /f
:: 若是设置用户环境变量,用%hkcu_env_root%
- 用powershell
; env_java.ps1
; help item
; 临时变量
$hkcu_env_root="Registry::HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment"
$hklm_env_root="Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Session Manager\Environment"
; Registry::HKEY_CURRENT_USER === HKCU:
; $hkcu_env_root="HKCU:\Environment"
; $hklm_env_root="HKLM:\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Session Manager\Environment"
; 查看已存在的环境变量
get-item $hkcu_env_root
get-item $hklm_env_root
; help Get-ItemProperty
; Get-ItemProperty -path $hklm_env_root -name TMP
Get-ItemProperty $hklm_env_root TMP
Get-ItemPropertyValue $hklm_env_root TMP
; 设置系统环境变量
; help Set-ItemProperty
; -type [String<REG_SZ>|ExpandString<REG_EXPAND_SZ>|Binary<REG_BINARY>|DWord<REG_DWORD>|MultiString<REG_MULTI_SZ>|Qword<REG_QWORD>]
; Set-ItemProperty -path $hklm_env_root -name JAVA_HOME -value "D:\\java\\jdk-15\\" -type string -force
Set-ItemProperty $hklm_env_root JAVA_HOME "D:\java\jdk-15" -type string -force
; 仅使用时%JAVA_HOME%会被替换实际值
Set-ItemProperty $hklm_env_root CLASSPATH ".;%JAVA_HOME%\lib" -type ExpandString -force
Set-ItemProperty $hklm_env_root Path "%JAVA_HOME%\bin;%Path%" -type String -force
; 若是设置用户环境变量,用$hkcu_env_root
Windows 中的注册表文件( system.dat 和 user.dat )是 Windows 的核心数据库。
REG文件实际上是一种注册表脚本文件,双击REG文件即可将其中的数据导入到注册表中。
注:路径分隔符不要用'/'。
5.2. 文件格式
<关键字>
<空行>
; 注释行
<注册表操作集合>
<空行>
<关键字>:一般是"Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00"。 若是Windows9X/ME/NT4.0是REGEDIT4。
<注册表操作集合>: 一般格式如下的一行或多行:
[注册表路径]
[-注册表路径]
[注册表路径\项名]
; REG_SZ的格式
"键名"="数据值"
[注册表路径\项名]
; 非REG_SZ的格式
"键名"=数据类型:新数据值
[注册表路径\项名]
"键名"=-
PS: 当数据类型是非REG_GZ,需要填入Hex值,可以用regedit随便创建一个项键值对,将值填入需要的数据,然后导出此项的reg文件,查看此文件中的键值内容。
5.3. 字符串与hex的互转用pwsh将字符串( reg_expand_sz 或 reg_multi_sz )与Hex( Hex(2) 或 Hex(7) )实现互转:
; reg_expand_sz => Hex(2)
; 单行实现
'hex(2):{0},00,00' -f (@( [System.Text.Encoding]::GetEncoding("utf-16").GetBytes("%tmp%;0123,abcd;中文;!@#$") | %{ $_.tostring('x2')} ) -join ',' )
; 分步实现
$str_value ="%tmp%;0123,abcd;中文;!@#$"
; $str_bin = @( $str_value.ToCharArray() | %{ ([int32]$_).ToString('x04') } | %{ '{1},{0}' -f $_.substring(0,2), $_.substring(2,2) } ) -join ','
$str_bin = @( [System.Text.Encoding]::GetEncoding("utf-16").GetBytes($str_value) | %{ $_.tostring('x2')} ) -join ','
$hex_value = 'hex(2):{0},00,00' -f $str_bin
"CONVERT '{0}' TO '{1}'" -f $str_value, $hex_value
; reg_multi_sz => hex(7)
; 单行实现
'hex(7):{0},00,00' -f ( ( @( [System.Text.Encoding]::GetEncoding("utf-16").GetBytes("%tmp%
0123
abcd
中文
!@#$
") | %{ $_.tostring('x2')} ) -join ',' ) -replace ',0a,00',',00,00' )
; 分步实现
$str_value = "%tmp%
0123
abcd
中文
!@#$
"
$str_bin = @( [System.Text.Encoding]::GetEncoding("utf-16").GetBytes($str_value) | %{ $_.tostring('x2')} ) -join ','
$hex_value = 'hex(7):{0}' -f ( $str_bin -replace ',0a,00',',00,00' )
"CONVERT '{0}' TO '{1}'" -f $str_value, $hex_value
; reg_expand_sz <= hex(2)
; 单行实现
[System.Text.Encoding]::GetEncoding("utf-16").GetString(@( ("hex(2):25,00,74,00,6d,00,70,00,25,00,3b,00,30,00,31,00,32,00,33,00,2c,00,61,00,62,00,63,00,64,00,3b,00,2d,4e,87,65,3b,00,21,00,40,00,23,00,24,00,00,00".Remove(0,7) -replace ',00,00$','') -split ',' | % { (Invoke-Expression "0x$_") } ))
; 分步实现
$hex_value = "hex(2):25,00,74,00,6d,00,70,00,25,00,3b,00,30,00,31,00,32,00,33,00,2c,00,61,00,62,00,63,00,64,00,3b,00,2d,4e,87,65,3b,00,21,00,40,00,23,00,24,00,00,00"
$hex_data = $hex_value.substring( 7 , $hex_value.length - 7 )
; $hex_data = "25,00,74,00,6d,00,70,00,25,00,3b,00,30,00,31,00,32,00,33,00,2c,00,61,00,62,00,63,00,64,00,3b,00,2d,4e,87,65,3b,00,21,00,40,00,23,00,24,00,00,00"
$hex_data = $hex_data.substring( 0, $hex_data.length - 6 )
$str_bytes = @( $hex_data -split ',' | % { (Invoke-Expression "0x$_") } )
$str_value = [System.Text.Encoding]::GetEncoding("utf-16").GetString($str_bytes)
; $str_value = @( ( $hex_data | Select-String '([0-9a-fA-F]{2},[0-9a-fA-F]{2})' -AllMatches ).matches.value | % { "0x{1}{0}" -f $_.substring(0,2),$_.substring(3,2)} | % { [char] (Invoke-Expression $_) } ) -join ''
; $str_value = @( [regex]::matches($hex_data, "(?i)([0-9a-fA-F]{2},[0-9a-fA-F]{2})") | %{$_.Groups[1].Value} | % { "0x{1}{0}" -f $_.substring(0,2),$_.substring(3,2)} | % { [char] (Invoke-Expression $_) } ) -join ''
"CONVERT '{0}' TO '{1}'" -f $hex_value, $str_value
; reg_multi_sz <= hex(7)
; 单行实现
[System.Text.Encoding]::GetEncoding("utf-16").GetString(@( ("hex(7):25,00,74,00,6d,00,70,00,25,00,00,00,30,00,31,00,32,00,33,00,00,00,61,00,62,00,63,00,64,00,00,00,2d,4e,87,65,00,00,21,00,40,00,23,00,24,00,00,00,00,00".Remove(0,7) -replace ',00,00$','') -split ',' | % { (Invoke-Expression "0x$_") } )) -split '\0'
; 分步实现
$hex_value = "hex(7):25,00,74,00,6d,00,70,00,25,00,00,00,30,00,31,00,32,00,33,00,00,00,61,00,62,00,63,00,64,00,00,00,2d,4e,87,65,00,00,21,00,40,00,23,00,24,00,00,00,00,00"
$hex_data = $hex_value.substring( 7 , $hex_value.length - 7 )
; $hex_data = "25,00,74,00,6d,00,70,00,25,00,00,00,30,00,31,00,32,00,33,00,00,00,61,00,62,00,63,00,64,00,00,00,2d,4e,87,65,00,00,21,00,40,00,23,00,24,00,00,00,00,00"
$hex_data = $hex_data.substring( 0, $hex_data.length - 6 )
$str_bytes = @( $hex_data -split ',' | % { (Invoke-Expression "0x$_") } )
$str_value = [System.Text.Encoding]::GetEncoding("utf-16").GetString($str_bytes)
$str_value = $str_value -split '\0'
"CONVERT '{0}' TO '" -f $hex_value; $str_value; "'"
- 在HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG下新建项new_item
[HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG\new_item]
- 删除HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG的项new_item
[-HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG\new_item]
- 在HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG\new_item下新建键new_key
[HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG\new_item]
"new_key"="a new key's value"
; 修改直接将key的填改为新值
- 删除HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG\new_item键new_key
[HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG\new_item]
"new_key"=-
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG\test]
@="我的默认字符串值"
"reg_sz"="%tmp%;0123,abcd;中文;!@#$"
"reg_binary"=hex:01
"reg_dword"=dword:00000020
"reg_qword"=hex(b):40,00,00,00,00,00,00,00
"reg_expand_sz"=hex(2):25,00,74,00,6d,00,70,00,25,00,3b,00,30,00,31,00,32,00,33,00,2c,00,61,00,62,00,63,00,64,00,3b,00,2d,4e,87,65,3b,00,21,00,40,00,23,00,24,00,00,00
"reg_multi_sz"=hex(7):25,00,74,00,6d,00,70,00,25,00,00,00,30,00,31,00,32,00,33,00,00,00,61,00,62,00,63,00,64,00,00,00,2d,4e,87,65,00,00,21,00,40,00,23,00,24,00,00,00,00,00
在文件上右击,出现的菜单项.
6.1.1. 注册表位置([...\*\])
;; 文件选中
; 系统
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\*\shell]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\${MyProgID}\shell\open]
; 右键上下文菜单
@="菜单文字"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\*\shellex\ContextMenuHandlers]
; 当前用户 和 本机
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Classes\*]
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\*]
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
; 文件上下文菜单: "用notepad 打开"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\*\shell\notepad ]
@="用notepad 打开"
"icon"="D:\\notepad \\notepad .exe"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\*\shell\notepad \command]
@=“D:\\notepad \\notepad .exe \"%1\"”
PS: 若仅配置当前用户或本机,请修改为其对应的注册表位置.
6.1.3. 配置指定扩展名文件上下文菜单<文件>6.2. 目录上下文菜单
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 ; MyProgID 配置 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\${MyProgID}\DefaultIcon] @="${MyProgID}.ico" [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\${MyProgID}\shell\open] ; 右键上下文菜单 @="用${MyProgID}打开" [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\${MyProgID}\shell\open\command] @="\"${MyProgID}.exe\" \"%1\"" ; .myext关联${MyProgID}且有上下文菜单 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.myext] @="${MyProgID}" [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.myext\OpenWithProgids] "${MyProgID}"=hex(0):在目录上或当前目录空白处右击,出现的菜单项.
6.2.1. 注册表位置([...\Directory])6.2.2. 配置wt(Windows Terminal)上下文菜单<目录>
;; 系统 ; 目录选中 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell] [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shellex\ContextMenuHandlers] ; 当前目录空白处 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\Background\shell] [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\Background\shellex\ContextMenuHandlers] ;; 当前用户 和 本机 [HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Classes\Directory] [HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Classes\Directory\Background] [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\Directory] [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\Directory\Background]
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 ;; 右键菜单 ; 右键目录(已选中)菜单 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\wt] ; 菜单名称 @="Windows Terminal" ; 图标 "Icon"="D:\\mylink\\wt\\terminal.ico" [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\wt\command] ; 执行命令 @="C:\\Users\\wuxr\\AppData\\Local\\Microsoft\\WindowsApps\\wt.exe -d %V" ; 目录(未选中)右键菜单 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\Background\shell\wt] @="Windows Terminal" "Icon"="D:\\mylink\\wt\\terminal.ico" [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\Background\shell\wt\command] @="C:\\Users\\wuxr\\AppData\\Local\\Microsoft\\WindowsApps\\wt.exe -d %V" ; 以管理员身份运行 HKEY_CURRENT_USER 或 HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE [HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\AppCompatFlags\Layers] "C:\\Users\\wuxr\\AppData\\Local\\Microsoft\\WindowsApps\\wt.exe"="~ RUNASADMIN"PS: 若仅配置当前用户或本机,请修改为其对应的注册表位置.
7. 文件关联将扩展名的文件关联一个或多个程序,会呈现默认关联程序图标,双击直接打开,右击出现"打开方式..."选择关联程序打开.
词条说明:
7.1. 注册表位置([...\.myext\])
- 图标 = 呈现关联程序图标
- 打开方式 = 右击文件出现"打开方式..."选项
- 双击打开 = 双击文件由关联程序或选择某个关联程序打开
假定扩展名是.myext。
7.2. 已存在的程序ID注册表配置
; 系统 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.myext] ; 当前用户 [HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\FileExts\.myext] ; 程序ID [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\${程序ID}] [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Applications\${程序ID}]假设应用程序notepad ,notepad,vscode都已安装正常,并已存在下面的注册表内容.
7.3. 配置扩展名的关联程序
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 ;; 程序ID ; [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\${程序ID}] ; [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Applications\${程序ID}] ;; notepad ; ID=Notepad _file [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Notepad _file] [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Notepad _file\SupportedTypes] ; ".myext"="" [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Notepad _file\shell\open\command] @="\"D:\\notepad \\notepad .exe\" \"%1\"" ; ID=notepad .exe [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Applications\notepad .exe] [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Applications\notepad .exe\shell\open\command] @="\"D:\\notepad \\notepad .exe\" \"%1\"" ;; VSCODE ; ID=vscode [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\vscode] [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\vscode\shell\open\command] @="\"D:\\VSCode-win32-x64\\Code.exe\" --open-url -- \"%1\"" ; ID=Code.exe [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Applications\Code.exe] [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Applications\Code.exe\shell\open\command] @="\"C:\\Users\\wuxr\\AppData\\Local\\Programs\\Microsoft VS Code\\Code.exe\" \"%1\"" ;; notepad ; ID=notepad.exe [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Applications\notepad.exe] [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Applications\notepad.exe\shell\open\command] @="%SystemRoot%\system32\notepad.exe %1" ;; command=程序 参数... 支持环境变量(%var%),位置参数(%n),特殊符号(\")需转义 ; "\"D:\\notepad \\notepad .exe\" \"%1\"" ; "%SystemRoot%\system32\notepad.exe %1" ; "\"D:\\VSCode-win32-x64\\Code.exe\" --open-url -- \"%1\"" ; "\"C:\\Users\\wuxr\\AppData\\Local\\Programs\\Microsoft VS Code\\Code.exe\" \"%1\""下面是扩展名(.myext)的文件,配置关联程序(notepad ,notepad,vscode)的注册表配置.
7.3.1. 全局扩展名关联扩展名关联配置对所有用户有效.
- 关联方法1
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 ;;; 关联方法1:默认链接已存在的程序ID(仅限[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\]下) ;; .myext默认关联包括: 图标, 打开方式,双击打开 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.myext] ; 程序ID(仅[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Notepad _file]) ; @="${程序ID}" ; 等同于链接 @="Notepad _file"
- 关联方法2
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 ;;; 关联方法2:新建并关联程序 ;; .myext默认关联包括: 图标,双击打开 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.myext\DefaultIcon] @="\"D:\\notepad \\notepad .exe\",0" [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.myext\shell\open\command] ; 程序(D:\\notepad \\notepad .exe) @="\"D:\\notepad \\notepad .exe \" \"%1\"" ; [-HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.myext\shell]
- 关联方法3
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 ;;; 关联方法3:OpenWithProgids链接已存在的程序ID(仅限[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\]下) ;; .myext默认关联包括: 图标, 打开方式,双击打开 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.myext\OpenWithProgids] ; 程序ID(仅[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\${程序ID}]) 叠加OpenWithList ; "${程序ID}"=hex(0): ; 等同于链接 "Notepad _file"=hex(0): "vscode"=hex(0):
- 关联方法4
7.3.2. 当前用户配置扩展名关联
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 ;;; 关联方法4:OpenWithList链接已存在的程序ID(仅限[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Applications\]下) ;; .myext默认关联包括: 打开方式 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.myext\OpenWithList] ; 程序ID(仅[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Applications\${程序ID}]) [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.myext\OpenWithList\notepad .exe] [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.myext\OpenWithList\notepad.exe] ; [-HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.myext\OpenWithList]扩展名关联配置仅对当前用户有效.
- 关联方法5
8. 参考资料
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 ;; 当前用户.myext的关联 [HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\FileExts\.myext] ;; .myext默认关联包括: 图标, 打开方式,双击打开 [HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\FileExts\.myext\OpenWithProgids] ; 程序ID(仅[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\${程序ID}]) 叠加OpenWithList ; "${程序ID}"=hex(0): ; 等同于链接 "Notepad _file"=hex(0): "vscode"=hex(0): ;; .myext默认关联包括: 双击打开选择关联程序 [HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\FileExts\.myext\OpenWithList] ; 程序ID(仅[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Applications\${程序ID}]) "a"="notepad .exe" "b"="notepad.exe" "MRUList"="ab" ;[-HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\FileExts\.myext],
- 高级用户的 Windows 注册表信息
- 如何使用-reg-文件添加-修改或删除注册表子项和值
- powershellcore(pwsh)参考
- powershell关于正则
- Powershell: The many ways to use regex





