Java是在1990年由James Gosling创建的,其初衷是作为智能设备(如交互式电视、无所不能的烤箱、时间旅行的终结者、奴役人类的SkyNet军用卫星等)的大脑。Gosling对其使用C 编写的程序感到失望,他灵机一动,决定躲在办公室开发一种更适合其需求的新语言。

当时交互式电视已成为一个具有数百万美元产值的行业,该语言成为公司进入该行业的发展策略的一部分。可到今天这些都没成为现实(尽管Netflix、Hulu以及其他公司都在向游戏领域进军),但Gosling发明的新语言却发生了重大变化。
正当Oak开发小组即将被放弃之时,Web开始流行起来。正是阴差阳错,使Gosling发明的语言适合家用电器的特性也使其适用于Web。Gosling的团队设计了能够让程序在Web页面安全运行的方法,而且为了与该语言的新用途相匹配,为之选了一个引人注目的新名字:Java。
Java语言的最初目标之一就是要比C 容易掌握,James Gosling于20世纪90年代在他的智能家电项目中使用的就是C 。Java的很大一部分都是基于C 的,因此学习过C 语言编程的人学习起Java来也不困难。然而,C 中有些难以学习和难以正确使用的内容已经从Java中删除。
Android成为Java语言使用最为广阔的一个领域。在掌握了Java语言之后,你可以使用Android软件开发包(SDK)开发自己的app。Android SDK是一款可以在Windows、Mac OS和Linux上运行的免费编程套件。
1 jdk下载和安装下载地址(下载时要用邮箱申请一个帐号):
https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/#java8-windows
jdk-8u321-windows-i586.exe 162M
安装:
1.1 可选组件

1.2 可在安装完成后访问教程:

https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/

安装后文件夹大小:

安装好JDK后就可以用cmd来编译和运行java程序了。
编译.java使用javac.exe,编译后生成同名.class(跨平台),用java.exe运行,两个程序如下安装路径:
"C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_321\bin\javac.exe"
"C:\Program Files\Java\jre1.8.0_321\bin\java.exe"
2 windows 7 32位平台下第一个java程序(在CMD下编译、运行)ref:
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/getStarted/cupojava/win32.html
2.1 Create a Source File,扩展名为.java
class HelloWorldApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!"); // Display the string.
}
}
2.2 Compile the Source File into a .class File
windows徽标键 R,运行CMD,输入:
"C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_321\bin\javac.exe" "f:\java\HelloWorldApp.java"
路径有空格,加上双引号。
在.java相同路径下生成同名.class文件。
2.3 run .class file
再在CMD输入:cd \d f:\java
使用.java所在路径为CMD当前路径,再输入:
"C:\Program Files\Java\jre1.8.0_321\bin\java.exe" "HelloWorldApp"
即可运行.class文件。

2.4 配置环境变量(简化路径输入)
以上运行java.exe和javac.exe老是要在前面加一串路径字符串,不方便,这就要配置环境变量了,这样在CMD直接输入java和javac时,CMD就会在环境变量指示的路径下搜索java和javac的路径,以确定是不是内部变量和外部程序。
2.4.1 将javac.exe所在路径配置到path

2.4.2 将java.exe所在路径配置为JAVA

如果是Vista、Win7、Win8系统,使用鼠标右击“计算机”->属性->左侧高级系统设置->高级->环境变量
系统变量->新建->变量名:JAVA_HOME 变量值:JDK安装目录
系统变量->新建->变量名:CLASSPATH 变量值:.;%JAVA_HOME%\lib
系统变量->编辑->变量名:Path 在变量值的最前面加上:%JAVA_HOME%\bin;
至于exe文件?为什么要用java来做exe文件?java的核心是它的跨平台,而exe只是运行在win环境下。
3 netbeans尽管可以只使用Java开发工具包(JDK)和文本编辑器来开发Java 程序,但是如果使用IDE,由此带来的编程体验会更好。
NetBeans是Oracle为Java程序员提供的一款免费IDE,它可以更容易地组织、编写、编译和测试使用Java开发的软件。NetBeans集成了编辑器、图形界面编译、调试、运行等工具,包含一个项目和文件管理器、图形用户界面设计器,以及许多其他工具。它的一个杀手级特性是用户在输入代码时,其代码编辑器能够自动检测到Java语法错误。
3.1 下载
https:///s/1qYZFRre#list/path=/
netbeans-8.2-windows.exe:231M
3.2 安装
安装时会检查是否安装了JDK,需要先安装JDK。

NetBeans对3个版本的Java语言都提供支持,这3个版本是:JavaStandard Edition(JSE)、Java Enterprise Edition(JEE)和JavaMobile Edition(JME)。它还支持Web应用开发、Web服务和JavaBeans。
Java Enterprise Edition是Java Standard Edition的一个扩展,它包含了支持Enterprise JavaBeans、XML处理和servlet开发的包,其中servlet是运行在Web服务器上的Java程序。Java EE还包含一个应用服务器,这是一个复杂的环境,用来执行专门为企业和其他大型组织开发的具有大量计算需求的Java软件。

筛选后可以减少安装大小:

安装后文件夹大小:

4.1 新建项目:

输入项目名称:
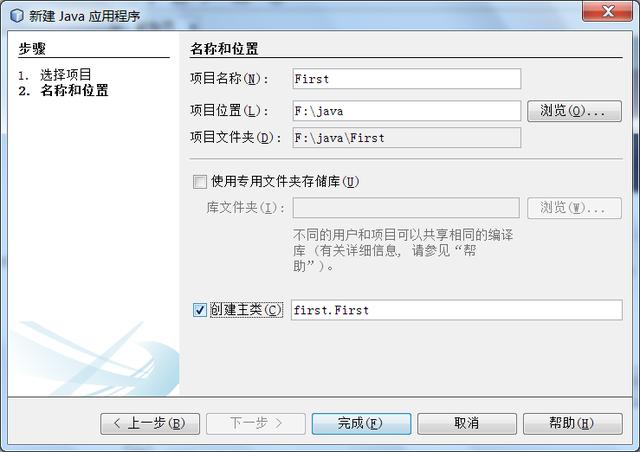
自动生成框架代码:

项目文件和文件夹:

源文件:

4.2 编译、及编译后的项目和文件夹:
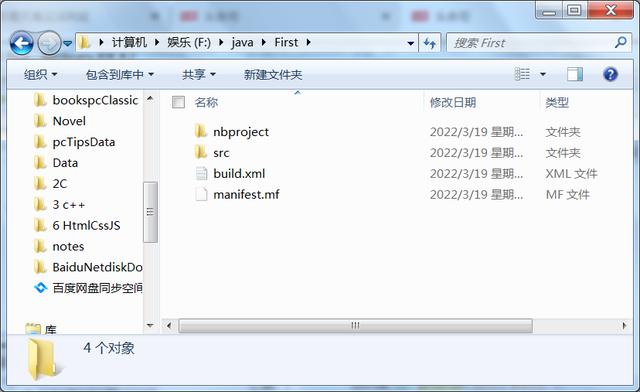
编译文件:

4.3 运行

https://www.onlinegdb.com/

https://tool.lu/coderunner/

https://www.bejson.com/runcode/java/

demo(体会与C 语法的区别):
package first; // 用包组织类
// to group classes in a collection called a package.
// The standard Java library is distributed over a number of packages,
import java.util.*; // #include using namespace others
import java.io.*;
public class First { // C 类是全局的,无修饰
// Everything in a Java program must be inside a class.
// every class in Java extends Object.
// A source file can only contain one public class,
// and the names of the file and the public class must match.
private String city;
int ivar; // default scope: package
public static void main(String[] args) { // 一个程序需要某个类有main方法
// 任何Java程序都是一个类,拥有main的称为主类
// 主类,程序名与类名一致时,
// 其它类,可有main,用于单元测试,
//System.out.println(args[0]);// bound checking, not program itself
int $var = 3; // C 变量只能以字母和下划线开头
String str = "abc"; // C string是模板类的typedef
byte i = 3; // byte,取值范围为−128~127的整数,signed char
boolean b = true; // bool
final int FIELDGOAL = 3;// const
int bit = 0b01011; //
System.out.println(str "def" bit i b);// 隐式转换,C printf()
System.out.printf("%8.5f\n",1/0.618);
String declar; // only declaration
declar = new String("abc");
System.out.println(declar);
// switch不只是整型
String command = "BUY";
int balance = 550;
int quantity = 42;
switch (command) {
case "BUY":
quantity = 5;
balance -= 20;
break;
case "SELL":
quantity -= 5;
balance = 15;
}
// A constant expression of type char, byte, short, or int
// An enumerated constant
// Starting with Java SE 7, a string literal
System.out.println("Balance: " balance "\n"
"Quantity: " quantity);
// time
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(startTime);
// c : time_t first = time(NULL);
// 数组
int[] arr = new int[25]; // int *arr = new int[25];
// 对象与类型转换
// Java中的所有对象都是Object类的子类
String[] names = {"Spanky", "Alfalfa", "Buckwheat", "Daria",
"Stymie", "Marianne", "Scotty", "Tommy", "Chubby"};
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); // vector<int> arr[25];
// the angle brackets cannot be a primitive type
for (i = 0; i < names.length; i ) {
list.add(names[i]);
}
Collections.sort(list);
for (String name : list){
System.out.println(name);
}
int[][] magicSquare = {
{16, 3, 2, 13},
{5, 10, 11, 8},
{9, 6, 7, 12},
{4, 15, 14, 1}};
for (i = 0; i < magicSquare.length; i )
{
for (int j = 0; j < magicSquare[i].length; j ) {
System.out.printf("%d ",magicSquare[i][j]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
//System.out.printf("%d ",magicSquare[8][8]);// bounding checking
// 哈希类
HashMap phonebook2 = new HashMap(30, 0.7F); // 初始容量和负载因子
HashMap<String, Integer> phonebook = new HashMap<>(); // 指明键和值的类
phonebook.put("Butterball Turkey Line", 80028883);
int number = phonebook.get("Butterball Turkey Line");
File cookie = new File("cookie.web");
try (FileInputStream stream = new FileInputStream(cookie)) {
System.out.println("Length of file: " cookie.length());
} catch (IOException ioe) {
System.out.println("Could not read file.");
}
// lambda
Comparator<String> comp
= (first, second) // Same as (String first, String second)
-> first.length() - second.length();
// object
// java data type
Integer xx = 17; // Autoboxing (int -> Integer)
int aa = xx; // Unboxing (Integer -> int)
Moden md = new Moden(80);// All Java objects live on the heap
System.out.println(md.speed);
Demo.staticFunc();
Demo de = new Demo(); // return a object reference
de.instanceFunc();
/*
1 primitive types: boolean, byte, char, double, float, int, long, short;
2 reference types: A class type, interface type, or array type, such as String,
Charge, Comparable, or int[]. A variable of a reference type stores
an object reference, not the data-type value itself.
3 wrapper types: A reference type corresponding to one of the primitive types,
such as Boolean, Btye, Character(char), Double, Float, int(Integer), Long, Short.
Java automatically converts between an object from a wrapper type
and the corresponding primitive data-type value—in assignment statements,
method arguments, and arithmetic/logic expressions.
pass by value: Java's style of passing arguments to methods—
either as a data-type value (for primitive types)
or as an object reference (for reference types).
*/
// interface instance, lambda
double res = integrate(new GaussianPDF(), -1, 1, 1000);
System.out.println(res);
res = integrate(x -> x*x, 0, 10, 1000); // lambda expression
System.out.println(res);
}
public static double integrate(Function f,
double a, double b, int n) {
double delta = (b - a) / n;
double sum = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ) {
sum = delta * f.evaluate(a delta * (i 0.5));
}
return sum;
}
}
// 继承
class Moden {
int speed;
public Moden(int i) {
speed = i;
}
}
class cableModen extends Moden { // :public, All inheritance in Java is public inheritance
public int size;
public cableModen(int speed,int size){ // :Moden(speed){this.size = size;}
super(speed);
this.size = size;
}
}
abstract class Comparable2
{
private String datafiled;
public abstract int compareTo(Object other); //
}
// an abstract method is called a pure virtual function and is tagged with a trailing = 0
interface Comparable
{
int compareTo(Object other); // All methods of an interface are automatically public.
default int compareTo2(Object other) { return 0; }
// By default, all elements are the same
}
class Demo{
public static void staticFunc(){
System.out.println("class method(static, class call)!");
}
public void instanceFunc(){
System.out.println("Instance method(object call)!");
}
}
interface Function
{
public abstract double evaluate(double x);
}
class Square implements Function
{
public double evaluate(double x)
{ return x*x; }
}
class GaussianPDF implements Function
{
public double evaluate(double x)
{ return Math.exp(-x*x/2) / Math.sqrt(2 * Math.PI); }
}
class LinkedStackOfStrings {
private Node first;
private class Node {
private String item;
private Node next;
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{ return (first == null); }
public void push(String item)
{ // Insert a new node at the beginning of the list.
Node oldFirst = first;
first = new Node();
first.item = item;
first.next = oldFirst;
}
public String pop() { // Remove the first node from the list and return item.
String item = first.item;
first = first.next;
return item;
}
}
/* Supplying instance fields and methods that operate on them
is the job of the classes that implement the interface.
being similar to an abstract class with no instance fields.
*/
/* Why can’t Comparable simply be an abstract class?
A class can only extend a single class(not support multiple inheritance.
But each class can implement as many interfaces.
C has multiple inheritance, similar to a Java class with a single superclass
and additional interfaces.
*/
// dynamic binding is the default behavior;
// if you do not want a method to be virtual, you tag it as final.
// Unlike C , Java has no programmable operator overloading.
// Since Java does automatic garbage collection,
// manual memory reclamation is not needed, so Java does not support destructors.
// implements将类声明为支持一个或多个监听接口 支持Runnable接口
// class LoadStocks implements Runnable {} //
// C virtual function override, implement abstract class
// 通过调用Thread构造函数创建线程化类的对象;
// 通过调用start()方法启动线程。
附Java简史:
1996年1月,Sun公司发布了Java的第一个开发工具包(JDK 1.0)。
1998年12月8日,第二代Java平台的企业版J2EE发布(Enterprise Edition)。
2004年9月30日,J2SE1.5发布,成为Java语言发展史上的又一里程碑。为了表示该版本的重要性,J2SE 1.5更名为Java SE 5.0(内部版本号1.5.0),代号为“Tiger”,Tiger包含了从1996年发布1.0版本以来的最重大的更新,其中包括泛型支持、基本类型的自动装箱、改进的循环、枚举类型、格式化I/O及可变参数。
2009年,甲骨文公司宣布收购Sun。
2014年,甲骨文公司发布了Java8正式版。新增lambda表达式、提供函数式接口。
2017年9月22 日,Java 9正式发布,带来了很多新特性,其中最主要的变化是已经实现的模块化系统。此后,半年一次版本迭代。
Java SE 10 2018-03-14
Java SE 11 2018-09-26,长期支持版本(LTS, Long-Term-Support),将会获得 5 年的技术支持。
Java SE 12 2019-03-20
Java SE 13 2019-09-17
Java SE 14 2020-03-17
Java SE 15 2020-09
Java SE 16 2021-03
Java SE 17 2021-09,长期支持版本,将会获得 8 年的技术支持。
附关键字:

ref:
https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/
https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/1612d500968640e20e1eeebb.html
https://baike.baidu.com/item/jdk/1011
-End-
,




